CST, or Central Standard Time, is one of the major time zones used in North America and several other regions worldwide. It is 6 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−6) and plays a crucial role in scheduling, broadcasting, business, and daily life for millions of people.
Understanding CST is essential for travel, communication across regions, and coordinating events in a globalized world.
What Is CST?
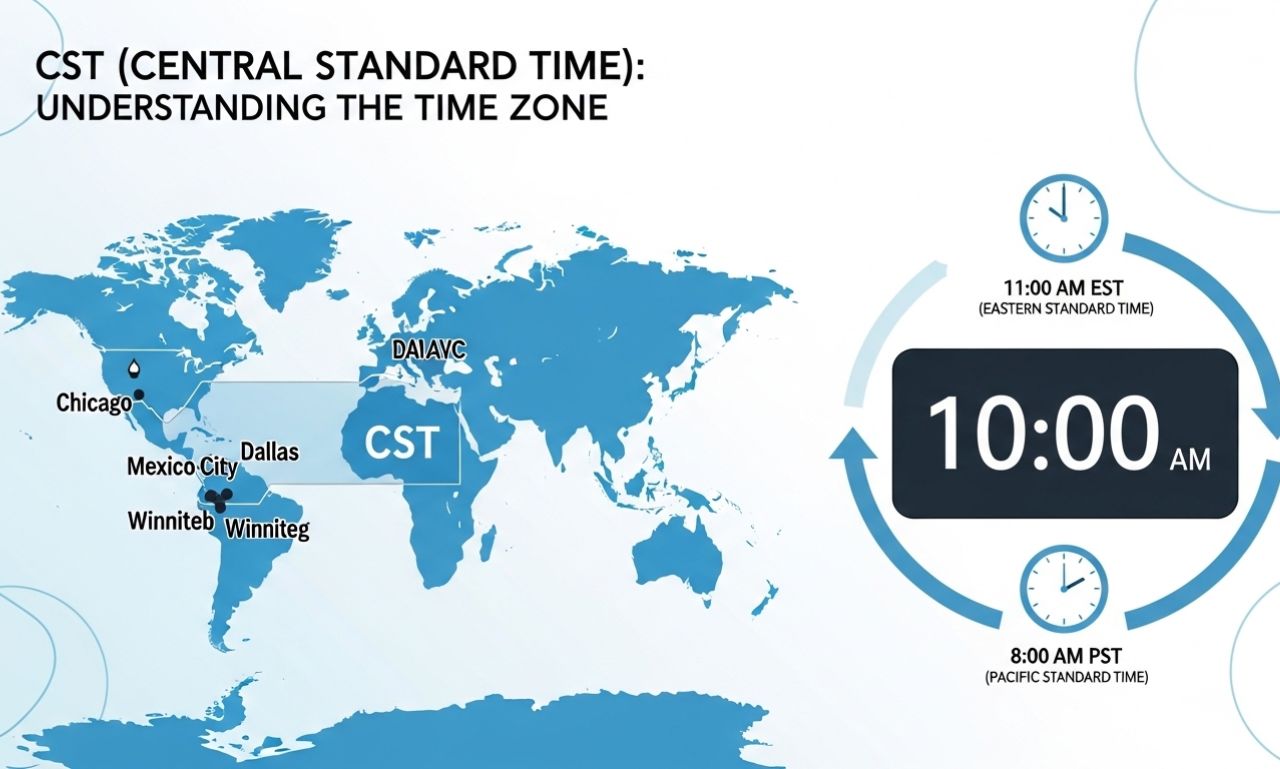
Central Standard Time (CST) is the time standard used in the central part of the United States, Canada, Mexico, Central America, and parts of the Caribbean. It is one hour behind Eastern Standard Time (EST) and one hour ahead of Mountain Standard Time (MST).
CST operates on UTC−6 during the standard time period. During daylight saving time, many CST regions switch to Central Daylight Time (CDT, UTC−5) to make better use of daylight.
Regions That Use CST
CST is widely used across North and Central America. Some notable regions include:
-
United States – Cities like Chicago, Dallas, Houston, and Minneapolis.
-
Canada – Provinces such as Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and parts of Ontario.
-
Mexico – Central parts including Mexico City and Guadalajara.
-
Central America – Belize, Honduras, Costa Rica, and Nicaragua.
-
Caribbean – Some territories follow CST for business and communication.
These areas rely on CST for official timekeeping, media scheduling, and public services.
CST vs. Other Time Zones
Understanding CST’s relation to other time zones is important for communication:
-
C ST vs EST – C ST is 1 hour behind Eastern Standard Time.
-
C ST vs PST – CST is 2 hours ahead of Pacific Standard Time.
-
C ST vs GMT/UTC – C ST is 6 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time.
This knowledge is critical for businesses, travel planning, and digital meetings across different regions.
Daylight Saving Time
Most regions observing CST also implement Daylight Saving Time (DST), switching to Central Daylight Time (CDT) typically from March to November. During this period, clocks are set forward by one hour (UTC−5) to maximize daylight during evenings.
This shift affects scheduling for airlines, broadcasts, and international meetings, so awareness of DST changes is crucial.
Technology and Daily Life
C ST is integrated into many aspects of daily life:
-
Digital Devices – Smartphones, computers, and smart devices automatically adjust for C ST and daylight saving time.
-
Broadcasting – TV and radio schedules often list C ST to guide viewers in central regions.
-
Business and Travel – Coordinating meetings or flights between C ST and other zones requires accurate knowledge of time differences.
-
Events and Sports – Many sports leagues and live events provide times in C ST for central audience clarity.
Tips for Converting CST to Other Time Zones
-
Use online converters – Websites and apps provide real-time conversion.
-
Know the offset – C ST = UTC−6, CDT = UTC−5.
-
Check daylight saving time – Some regions may not observe DST.
-
Plan for global meetings – Always confirm participants’ local times to avoid confusion.
Conclusion
C ST (Central Standard Time) is more than just a time zone — it’s a critical reference point for millions of people in North and Central America. Whether for business, travel, broadcasting, or daily life, understanding C ST helps maintain punctuality, coordination, and seamless communication.
By knowing the regions, conversions, and daylight saving rules, anyone can effectively manage schedules and interactions across C ST and other global time zones.