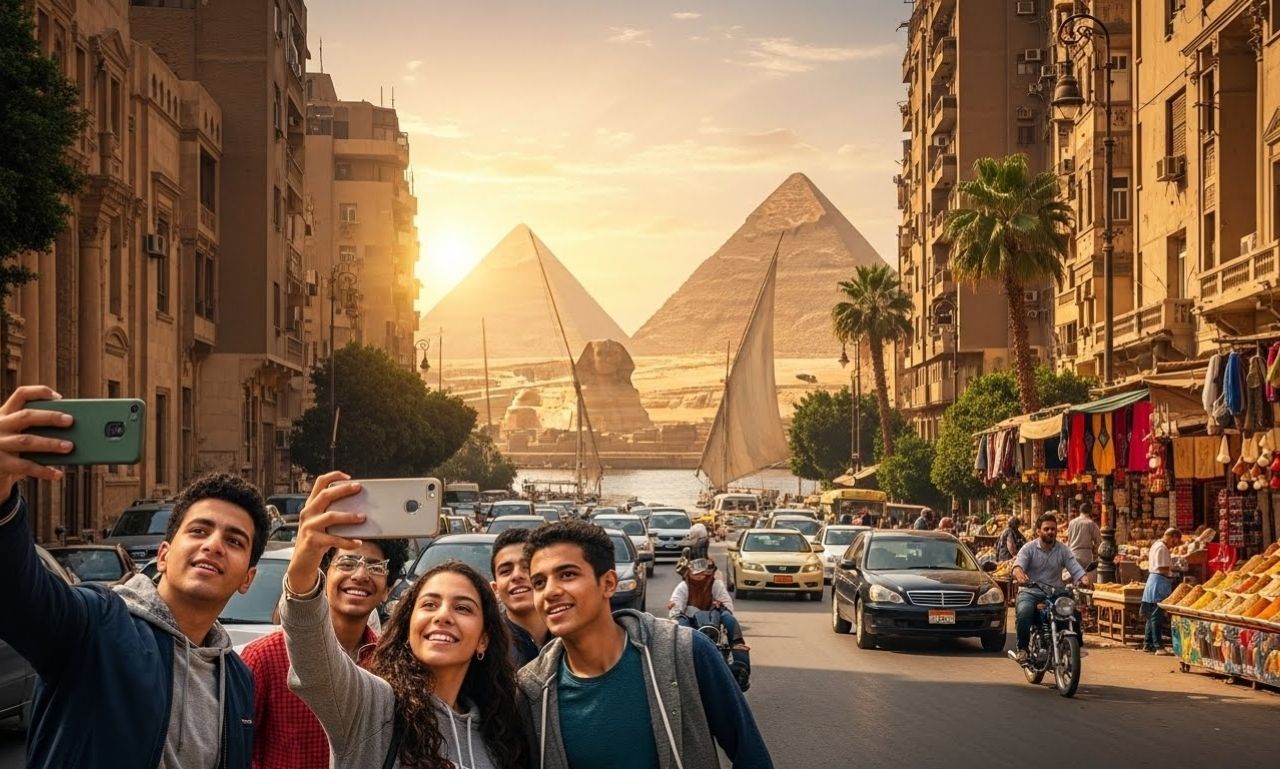
Egypt is one of the world’s most fascinating countries, known for its ancient civilization, iconic monuments, and lasting influence on human history. Located in North Africa and connecting Africa with the Middle East, Egypt has played a central role in trade, culture, and politics for thousands of years. From the majestic pyramids to the bustling streets of Cairo, Egypt represents a unique blend of tradition and modern development.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of Egypt, covering its history, geography, culture, economy, and global importance while highlighting why the country continues to attract scholars, travelers, and investors alike.
Ancient History of Egypt
The Foundations of Egyptian Civilization
The story of Egy pt begins over 5,000 years ago along the banks of the Nile River. Ancient Egy pt is considered one of the earliest and most advanced civilizations in human history. The Nile provided fertile land, enabling agriculture, stability, and the rise of powerful dynasties.
Pharaohs ruled Egy pt with both political and religious authority, overseeing the construction of temples, tombs, and monuments that still stand today. The pyramids of Giza, the Sphinx, and the Valley of the Kings are enduring symbols of ancient Egy ptian engineering and belief systems.
Geography and Natural Features of Egypt
The Role of the Nile River
Geography has always shaped Egy pt’s development. The Nile River runs from south to north, creating a narrow strip of fertile land surrounded by desert. This natural layout influenced settlement patterns and agricultural practices for centuries.
Beyond the Nile Valley, Egy pt includes vast deserts such as the Western Desert and the Eastern Desert, as well as the Sinai Peninsula. These regions hold natural resources and strategic importance, contributing to Egy pt’s regional influence.
Culture and Traditions in Egypt
Language, Religion, and Daily Life
Modern Egy pt is culturally rich and diverse. Arabic is the official language, and Islam is the predominant religion, with a significant Christian minority. Religious traditions play a strong role in shaping social values, holidays, and community life.
Egy ptian culture is known for its hospitality, strong family ties, and respect for tradition. Music, dance, and storytelling are deeply rooted in daily life, while traditional foods such as koshari and ful medames reflect the country’s culinary heritage.
Egypt’s Economy and Key Industries
Agriculture, Energy, and Trade
The economy of Egy pt is one of the largest in Africa and the Middle East. Agriculture remains important, particularly along the Nile Delta, producing crops like wheat, rice, and cotton.
In recent decades, Egy pt has expanded into energy production, especially natural gas. The Suez Canal is another major economic asset, serving as one of the world’s most important shipping routes and generating significant revenue through global trade.
Tourism in Egypt
Historical and Modern Attractions
Tourism is a cornerstone of Egy pt’s economy. Millions of visitors travel each year to explore ancient temples, museums, and archaeological sites. The Pyramids of Giza, Luxor’s Karnak Temple, and Abu Simbel are among the most visited landmarks.
In addition to historical tourism, Egy pt offers Red Sea resorts, desert safaris, and cultural festivals. These attractions highlight the country’s ability to combine ancient history with modern leisure experiences.
Education and Knowledge Legacy of Egypt
From Ancient Learning to Modern Institutions
Egy pt has long been a center of knowledge and education. In ancient times, Egyptian scholars made advances in mathematics, medicine, and astronomy. The Library of Alexandria symbolized the pursuit of knowledge in the ancient world.
Today, Egypt continues this tradition with universities and research institutions that attract students from across the region. Education remains a key factor in national development and innovation.
Egypt’s Role in Regional and Global Affairs
Political and Strategic Importance
Due to its location, Egypt holds significant geopolitical importance. It connects Africa, Asia, and Europe through trade routes and diplomacy. Egypt has historically played a leadership role in the Arab world and continues to influence regional politics.
Peacekeeping efforts, international partnerships, and economic cooperation have strengthened Egypt’s global presence, making it a vital player on the world stage.
Modern Challenges and Development in Egypt
Population Growth and Urbanization
Like many developing nations, Egypt faces challenges such as rapid population growth, urban congestion, and resource management. Major cities like Cairo are expanding quickly, requiring investments in infrastructure, housing, and transportation.
The government has launched development projects, including new cities and renewable energy initiatives, aimed at improving quality of life and ensuring sustainable growth.
The Future of Egypt
Innovation and Sustainability
The future of Egypt lies in balancing tradition with progress. By investing in education, technology, and sustainable development, Egypt aims to strengthen its economy and preserve its cultural heritage.
Renewable energy projects, digital transformation, and tourism development are expected to play key roles in shaping Egypt’s long-term growth and stability.
Conclusion
Egypt is a country where ancient history and modern life coexist in remarkable harmony. From the legacy of the pharaohs to contemporary economic and cultural advancements, Egypt continues to captivate the world. Its strategic location, rich traditions, and resilient population ensure that Egypt remains a vital and influential nation.
Whether viewed through the lens of history, culture, or development, Egypt stands as a timeless symbol of human achievement and enduring civilization.